The domain name life cycle explains what happens to a domain from the moment it is registered until it expires, enters recovery stages, and becomes available again.
Why Understanding the Domain Name Life Cycle Matters
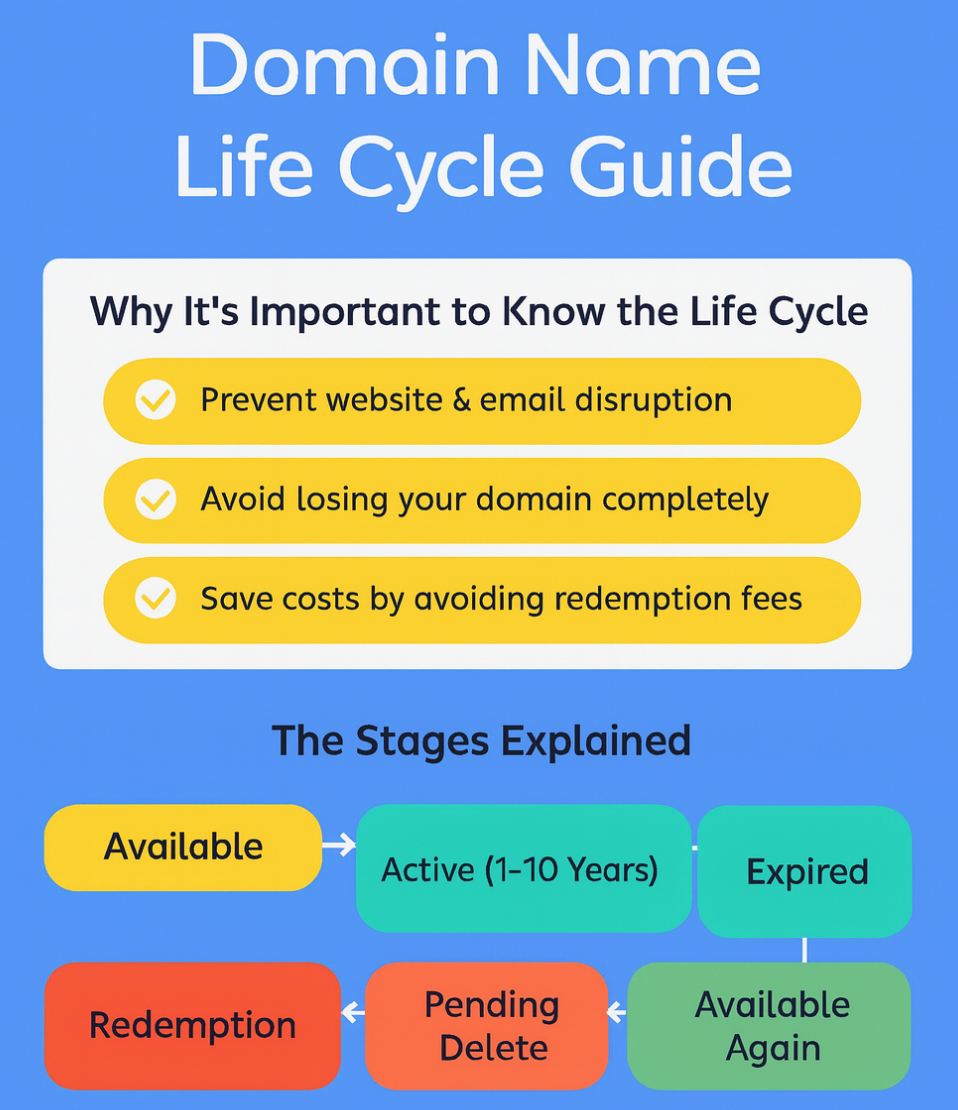
- Prevent Website & Email Downtime
Your domain controls how your website loads and how your email is delivered.
Once the expiry date passes, DNS begins to fail, and your services may stop working.
Knowing the cycle lets you act before an outage happens.
- Avoid Permanent Loss of Your Domain
If you miss all renewal windows, your domain reaches the Pending Delete stage and becomes unrecoverable.
Competitors, automated domain catchers, or unrelated third parties can register it the moment it drops.
Knowing the timeline prevents this irreversible outcome.
- Reduce Unnecessary Redemption Fees
Recovering a domain in Redemption costs much more because the registry imposes a recovery fee.
Understanding the stages ensures you renew during the normal grace period instead of paying penalties.
- Respond Correctly in Troubleshooting Situations
When a website suddenly goes down or a customer loses access, knowing which stage the domain is in helps you give the correct solution:
- Expired? → Renew normally
- In Redemption? → Recover with fee (SGD $180/one-time)
- Pending Delete? → Prepare to re-register (normally, you will not be able to know when it will be available. You will have to check the status of the domain daily using whois system)
- Already released? → Register immediately
This prevents wasted time and incorrect instructions.
- Mitigate Security & Branding Risks
An accidentally dropped domain can lead to:
- Phishing
- Brand impersonation
- Traffic hijacking
- SEO losses
- Customer confusion
Knowing the cycle protects your digital assets.
- Manage Domain Portfolios with Confidence
Businesses that own multiple domains need to track renewals and expiry windows.
Knowledge of the life cycle lets IT or marketing teams maintain consistent uptime and ownership.
The Domain Name Life Cycle Explained (Step-by-Step)
Every domain goes through the following stages:
Stage 1 — Available
The domain is free for anyone to register.
This is the starting point.
You can check the domain name availability from our search domain availability from our website.
Stage 2 — Active (1 to 10 Years)
The domain has been registered and is fully functional.
You can:
- Host websites
- Run email services
- Manage DNS
- Renew it anytime
This is the longest and most stable stage.
Stage 3 — Expired (Grace Period)
The domain’s expiry date has passed, but the owner still has rights to renew it.
What happens:
- Website and email will not work at this stage
- DNS stops resolving depending on registry rules
- Owner can still renew at normal price
- No penalty fee yet
Grace period: 0–25 days, depending on the TLD and registry.
Stage 4 — Redemption Period
If the domain is not renewed during the grace period, it moves into Redemption.
Characteristics:
- Domain is removed from DNS
- Website/email completely down
- Registry locks the domain
- Owner can still recover it
- Requires redemption fee + renewal fee
Redemption period: ~25 days from end of Grace Period
This is the last chance to recover, but at higher cost.
Stage 5 — Pending Delete
No further actions are possible.
- Cannot be renewed
- Cannot be restored
- Registrar has no control
- Domain will be deleted
Pending Delete lasts ~5-30 days from end of Redemption period
After this, the domain will drop into public availability.
Stage 6 — Released / Available Again
The domain becomes public for anyone to register.
High-value domains may be taken within seconds by automated systems.
Real-World Situations Where This Knowledge Is Useful
✔ Website suddenly goes offline
You can immediately verify whether the domain expired, check the stage, and give the correct recovery option.
✔ A client hands over their domain late
You can confirm whether the domain is still in an affordable recovery window or already unrecoverable.
✔ Business forgets to renew due to internal turnover
You can check whether it’s in Expired, Redemption, or Pending Delete and take the correct action.
✔ A company wants to acquire a taken domain
You can monitor the lifecycle and predict when it will drop.
✔ Managing multiple brand domains
You can schedule renewals and avoid accidental loss.
If the above is too much to reach, save this quick reference table to know how to handle the situation:
| Stage | Duration | What Happens | Can Recover? |
| Active | 1–10 years
Check whois to know the exact duration |
Domain in use | Yes |
| Expired | 0–25 days | DNS may fail, normal renewal still possible | Yes |
| Redemption | ~25 days from Expired Period | Removed from DNS, recovery fee applies | Yes (costly, about SGD 180/one-time) |
| Pending Delete | ~5-30 days from Redemption Period | No actions allowed | No |
| Released | Immediate | Public registration | No (only new registration) |
Conclusion
Knowing the domain life cycle helps you take the right action at the right time — whether to prevent downtime, avoid losing your domain, or recover it correctly if it expires.